Remote Server Deployment Using GitHub Actions
This tutorial shows how to deploy any app on a Linux server (e.g. Linode, Digital Ocean e.t.c)
Requirements.
- Linux Server
- GitHub Repository
Step 1 - Setup up SSH on Remote Server
To achieve this, you need to create an SSH key for GitHub Action. Login to your server.
Generate SSH by entering ssh-keygen, enter a new name if you have an existing key i.e. .ssh/github_action, continue
, and you should get a response like a sample below.
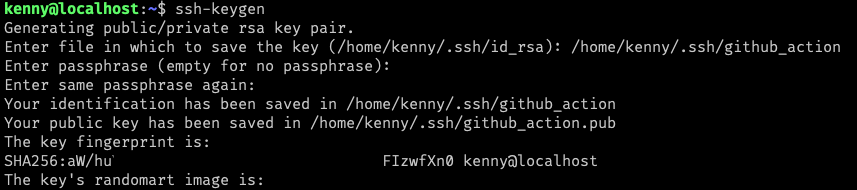
One final thing here is to cp github_action authorized_keys and then cat github_action.pub
Step 2 - Setup GitHub Action
Firstly, on the code repository, click on the Settings tab, click on the Secret -> Action -> New secret for
SSH_HOSTe.g. 187.9.0.9.9.9SSH_KEYe.g. (github_action)SSH_USERNAMEe.g. root (or user of the created SSH)
Note: Copy the SSH public key i.e. github_action.pub and paste the value for SSH_KEY.
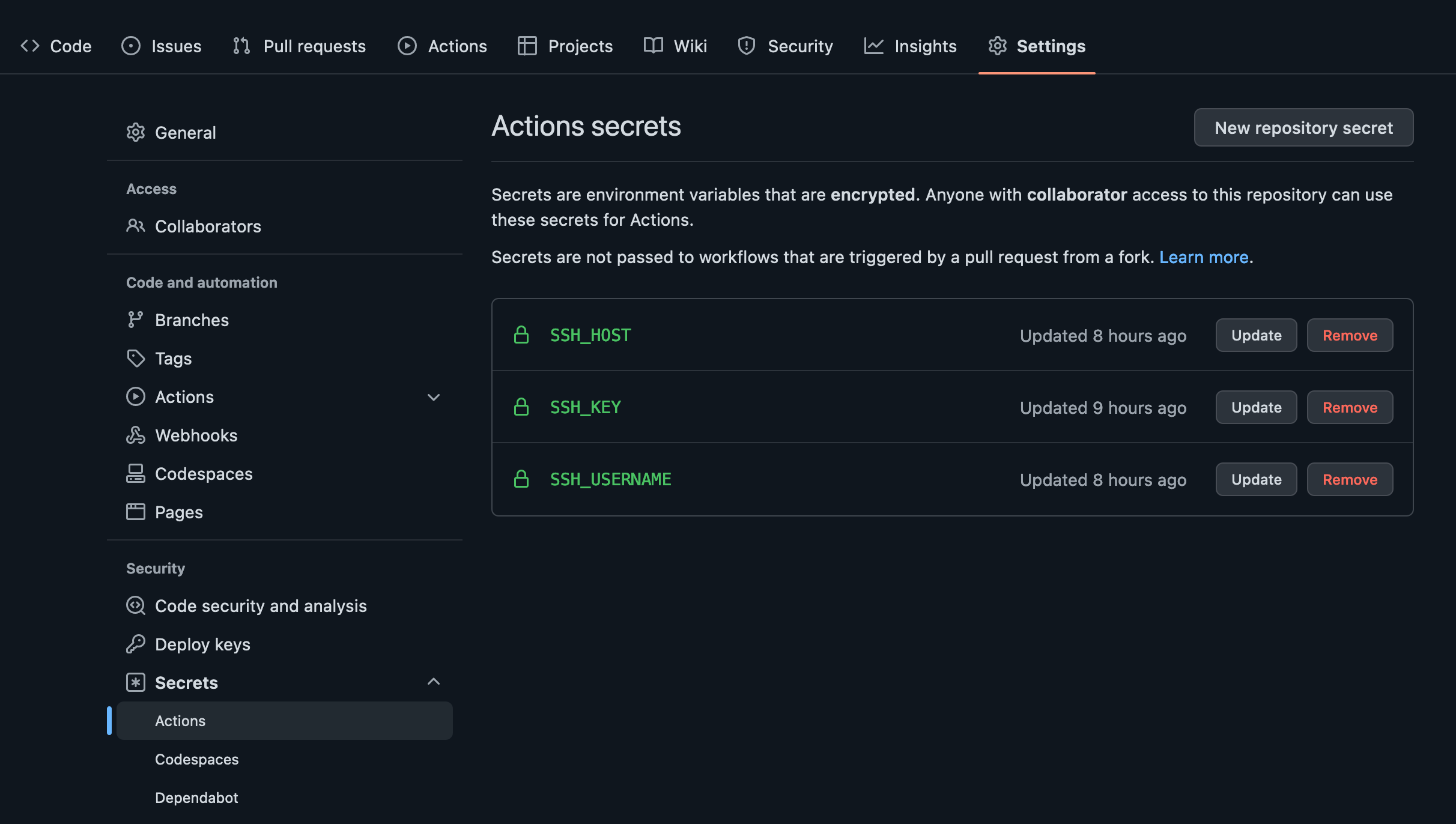
Click the action tab, then set up a workflow yourself.
You can give it any name you want, for this article, I will be using deployment.yml
# This is a basic workflow to help you get started with Actions
name: CI/CD Deployment to Remote Server
# Controls when the workflow will run
on:
# Triggers the workflow on push or pull request events but only for the "main" branch
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "main" ]
# Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
workflow_dispatch:
# A workflow run is made up of one or more jobs that can run sequentially or in parallel
jobs:
# This workflow contains a single job called "deploy"
deploy:
# The type of runner that the job will run on
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# Steps represent a sequence of tasks that will be executed as part of the job
steps:
# Checks out your repository under $GITHUB_WORKSPACE, so your job can access it
- uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.2
with:
host: ${{ secrets.SSH_HOST }}
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_KEY }}
username: ${{ secrets.SSH_USERNAME }}
script_stop: true
script: |
cd /var/www/html/
git pull origin main
# more command or scripts(shell) here
For more documentation on the workflow, check out appleboy/ssh-action
In a case when you need to run a sudo command on the remote server, add an ENV variable by clicking Settings tab, click on the Secret -> Action -> New secret
USER_PASSWORDi.e. your sudo password
then run the command like this echo $USER_PASSWORD | sudo -S systemctl start nginx
The -S (stdin) option causes sudo to read the password from the standard input instead of the terminal device.
Read more here
....
- uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.2
env:
GO_PASSWORD: ${{ secrets.USER_PASSWORD }}
MORE_VALUES: "....."
with:
....
envs: USER_PASSWORD,MORE_VALUES
script: |
echo $USER_PASSWORD | sudo -S systemctl start nginx
Step 3 - Commit and Run the Action
If the steps above are properly followed, the action should run each time you commit and push to main or merge a PR to main.
Happy Coding 👨🏾💻
If you find this useful, kindly share and repost. Thank you 😊!
